by Ivan | Sep 4, 2019 | Healthy Aging, Medical Conditions, Patient News
This Too Shall Pass: Treating and Preventing Kidney Stones
More common, frequently less painful and far more preventable than reputed, kidney stones have, entered a new era of highly effective, noninvasive procedures. We bring you up to date on kidney stone treatment & prevention
Q: Why do kidney stones happen?
A: They form when substances such as calcium, oxalate, cystine or uric acid are present at high levels in urine, becoming crystals that gradually increase in size to a stone. According to the Urology Care Foundation, Calcium stones are the most common (80%), with Uric Acid and Struvite / Infection stones making up the other 20%.
Q: How likely am I to experience kidney stones?
A: One in 10 people deal with kidney stones in their lifetime, more frequently men, but in recent years, women are rapidly closing the gap. Genetic factors also play a role: if kidney stones are prevalent among your family members, you are at higher risk of developing them.
Q: Are kidney stones very painful?
A: Over the years, the pain associated with kidney stones has taken on an almost mystical aura, sometimes described as “worse than childbirth.” However, the truth is that not every kidney stone causes intense pain. Some are small enough to pass unnoticed, and many are asymptomatic and only discovered when blood is found in the urine during routine testing. Others are large but can stay in the kidney forever without incident. It is only the stones that become “stuck” on their way out of the body that cause renal colic, or waves of severe pain, which can be promptly treated with pain medication.
Q: Does back pain mean I have kidney stones?
A: This is frequently asked by patients concerned about pain felt in the flank area near the kidney. A careful history will be taken to help determine the location of the pain, but a fairly simple way to distinguish the cause is to change positions. If the pain worsens, it is more likely to be a musculoskeletal type of strain. Kidney stone pain is less likely to be positional.
Q: How do you determine if treatment is needed?
A: A noninvasive, less expensive ultrasound is used for screening, but a spiral computed tomography (CT) scan provides superior imagery used to more accurately pinpoint the stone’s location. If only a partial obstruction is seen and not much pain is involved, time is on your side and we can wait to see if the stone passes naturally. At that point, many patients can rest comfortably at home and may be given antispasmodics (such as Flomax) to relax the ureter, pain medications to manage pain and instructed to drink plenty of water to aid the stone’s passage.
Q: What if it doesn’t pass on its own?
A: It’s reassuring to realize there is no urgency to remove the stone unless the kidney is obstructed or infected or the patient is experiencing intractable pain. And when removal is indicated, urologists (specialists in diseases of the urinary tract) have a number of options available, many of them noninvasive or minimally invasive. Open surgical procedures are a rare event. Instead, an outpatient ureteroscopy can be done, using an endoscope to break up or remove the stone. Even less invasive is lithotripsy, good for small stones, which directs high-energy shock waves toward the stone and breaks it into fragments to more easily pass out of the body. For extremely large or resistant stones, a minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy is conducted to remove the stone via an endoscope inserted through a small incision in the skin.
Q: What is the best way to prevent kidney stones from forming again?
A: We can take the time to develop an individualized approach, based on your stone’s composition. First, your stone will be tested and categorized as calcium oxalate (the most common type), calcium phosphate, a mix or a non-calcium type. Also recommended is a 24-hour urine collection to form a clear picture of how the crystals form in your body, as well as blood tests for further analysis. While those who have formed stones before are at higher risk for forming a subsequent one, we know that dietary modifications tailored to stone type and – if needed – drug therapy can substantially reduce that risk. If you form calcium oxalate stones, we’ll work on a plan to avoid foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, beets and rhubarb, and keep sodium consumption at a minimum. Also important to know is that despite its role in the stone’s composition, there is no need to restrict calcium. In fact, increasing your calcium intake with higher-calcium foods such as milk, yogurt and cheese can help lower oxalate levels in the urine. Finally, keep in mind that the single best preventive measure is to simply fill a bottle with water and drink often.
The post Kidney Stones: Treatment & Prevention appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.
by Ivan | Aug 1, 2019 | Nutrition, Patient News

Considering Keto: Is It the Right Diet for You?
The truth is that a silver bullet for weight loss likely does not exist, but Americans’ perpetual search continues unabated. Low-carb diets such as Paleo, Whole30, and most prominently, Ketogenics, or “keto” may be the latest contenders, yet Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics spokesperson Ginger Hultin, RD, reveals she’s never seen a more popular – or more misunderstood – trend, the Keto Diet…..
Keto’s guidelines dramatically change typical eating patterns, with an emphasis on high fats (accounting for 80% of daily calories); moderate proteins (10 to 20% of daily calories); restricted carbs (5 to 10% of daily calories – ideally 20 to 30 grams a day, or the equivalent of a medium apple); and elimination of all grains, starchy vegetables and high-carb fruits. This means a diet replete with meats, butter, seeds, avocado and oily fish, but little or no bread, potatoes, corn, beans, legumes, milk, beer, sugar or fruits like bananas and pears.
The concept, according to Hultin, is that getting most of your calories from fat forces the body to enter ketosis and burn stored fats. Here’s how: In the absence of circulating blood sugar, which comes from carbohydrates, the body starts breaking down stored fat into molecules called ketones via a process called ketosis. Once ketosis is reached, usually within three to four days of eating less than 20 to 50 grams of carbohydrates daily, ketones are used to generate energy in the body until carbohydrates are eaten again.
Earlier research showed ketosis has benefits for blood sugar control among people with diabetes, and its efficacy has been proven in controlling seizures in some patients with epilepsy. Most people are attracted to keto based on the promise of shedding pounds quickly, which is when the diet’s drawbacks become glaringly evident.
“When followed consistently for the short term, the keto diet can lead to rapid weight loss,” says Hultin. “However, when people stop following it, as is inevitable on a highly restrictive diet, the weight is just as quickly regained, plus more.”
Side effects of a keto diet range from constipation due to lack of fiber to a potential negative impact on liver and kidney function, and limiting vitamin- and mineral-rich fruits, vegetables and grains is a concern for sustaining heart health. Hultin believes keto’s limited choices can also be socially isolating to dieters.
“The keto diet may be a quick fix but is not a sustainable solution,” she says.
There is no debate around the life-changing aspects of the keto diet for young patients with epilepsy, but experts agree that the long-term effects on others warrant further research before recommendations can be made. For those still interested in trying keto, a focus on healthier fats is essential, rather than options such as bacon and cheese. Additionally, be sure to test and monitor your blood cholesterol levels, as studies show many keto dieters experience an unwanted increase in these numbers.
Other trendy diets may fare no better in terms of sustainability. Whole30 takes a deliberately short-term approach with a 30-day plan that eliminates all sugar, alcohol, grains, legumes and dairy and focuses on moderate amounts of meat, seafood and eggs; plenty of vegetables; some fruit; and natural fats. Most people return to their previous eating habits after the monthlong experiment, according to Mayo Clinic. A paleo diet focuses on foods that were hunted and gathered during the Paleolithic era, and typically includes lean meats, fruits, vegetables and nuts, but eliminates whole grains, legumes and dairy products, making it challenging to adopt long-term.
The ideal diet? One that places the greatest emphasis on nature’s bounty of fruits and vegetables; encourages whole foods, whole grains, healthy oils, moderate amounts of protein, and does not eliminate entire categories of food.
“Find a diet that’s flexible enough to let you feel good about your relationship with food … and enjoy your life!” advises Hultin.
Did You Know?
Because fasting can put a person into ketosis, intermittent fasting can also be considered a type of ketogenic diet.
The post Keto Diet: Right for You? appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.
by Ivan | Jul 9, 2019 | Patient News, Staying Active, Wellness

Wake-up Call: Fighting Fatigue at Its Roots
Feel like you are fighting fatigue throughout the day, the joy in life slowly diminishing and your active lifestyle becoming a distant memory? Are these ordinary signs of aging?
No, no and no!
Feeling tired all the time is not a normal part of the aging process. Instead, it can point to the need for a better night’s sleep, stress or an underlying illness, or be the result of a mix of common medications. Or it may be a combination of all these things. Identifying the possible sources of your fatigue is the most important step in reenergizing your lifestyle.
Medical: Visit your physician to rule out these frequently seen causes of tiredness.
Emotional health: Low-grade depression, anxiety or chronic stress can sap energy.
Anemia: This condition occurs when your blood has too few red blood cells or those cells have too little hemoglobin, a protein that transports oxygen through the bloodstream. If untreated, anemia results in a drop in energy levels.
Heart disease: When the heart pumps blood less efficiently, it can lead to fluid in the lungs, causing shortness of breath and reducing the oxygen supply to heart and lungs.
Hypothyroidism : An underactive thyroid gland can cause fatigue – along with other symptoms, such as weight gain, weakness, dry skin, feeling cold and constipation.
Medications : Many medicines can cause fatigue, including blood pressure drugs, antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs and antihistamines.
Lifestyle Habits
Sleep: Quality, quantity and environment matter greatly in ensuring a healthy sleep, but these factors are surprisingly misconstrued. According to NYU School of Medicine, dispelling these widely held beliefs is key:
- Myth: “Alcohol before bed is good for sleeping.” A nightcap before bed may help you fall asleep but will dramatically reduce the quality of sleep by disrupting the REM (rapid eye movement) stage all night, and you’ll wake unrefreshed.
- Myth: “Many adults need only five hours of sleep or less, especially as they get older.” The reality is everyone needs to get enough sleep to wake up feeling refreshed. The average is seven to eight hours nightly to allow the body to progress through four phases of restorative sleep, including deep sleep cycles of REM and delta waves sleep, which are important for generating neurons, repairing muscle and restoring the immune system.
- Myth: “Watching TV in bed before sleep is a good way to relax.” Actually, turning off the TV and putting away electronic devices at least two hours before bedtime is recommended, as the blue light produced affects the release of melatonin, the sleep hormone, and will delay slumber.
- Myth: “If I wake up in the middle of the night, it is best to lie in bed until I fall back asleep.” Tossing and turning for more than 20 minutes is not helpful; instead, change rooms and engage in something mindless, like folding socks. Do not watch TV or look at electronic devices, as this wakes up your brain.
- Myth: “Snoring is a common, harmless problem.” Snoring can be a sign of sleep apnea, a disorder characterized by decreased or complete lack of airflow throughout the night. Over time, this can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease if untreated.
- Myth: “Falling asleep anywhere, anytime is the sign of a good sleeper.” It’s just the opposite, indicating a sleep “debt” from insufficient rest or a sleep disorder such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea.
Under- or over-activity: Sedentary days and nights can cause loss of muscle mass and flexibility and make even moderately intense activities seem exhausting. However, exercising at a very high intensity can also cause fatigue.
An Infusion of Energy for Chronic Fatigue Research

Far beyond ordinary tiredness is the profound fatigue known as myalgic encephalomyelitis/ chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), which has puzzled and frustrated medical professionals for decades. No cure or approved treatment is available to its 2.5 million sufferers, only a management of symptoms worsened by any type of physical, cognitive or emotional effort. But a sea change is underway. It began in 2015 with a new name recommendation by the Institute of Medicine (IOM): Systemic Exertion Intolerance Disease (SEID). Noting that the term chronic fatigue syndrome can trivialize the seriousness of the condition and that “ME” is inappropriate because neither muscle pain nor brain inflammation has proven to be a symptom, the IOM panel stated: “SEID captures a central characteristic of this disease – that exertion of any sort can adversely affect patients in many organ systems and in many aspects of their lives.”
Even more promising is the significant investment in research announced by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Up to $36 million over five years has been granted to shine a brighter light on the origins and progression of chronic fatigue and ultimately to help develop diagnostic markers and effective treatments for fighting fatigue.
Did You Know?
58% of older adults sleep less than seven hours a night.
80% of people age 55 and over report unintentionally falling asleep at least once during the day within the last month.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The post Fighting Fatigue appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.
by Ivan | Apr 2, 2019 | Healthy Aging, Patient News, Staying Active
Ramping Up your Sprint Fitness after a Long, Sedentary Winter
Whether you went into hibernation as the result of a record cold winter season, or took time off from your usual exercise routine because of a busy schedule or illness, spring is an ideal time to get back in action. When done with care, starting or rebooting your fitness regimen this spring will set you up for a vibrant, energetic summer. After being cleared for exercise by our office, consider these issues to ensure you’re not sidelined by injury, fatigue or boredom and get the most out of your spring fitness efforts
Aerobic or strengthening exercise?
Both. According to the 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, any amount is helpful but the recommendations to help prevent chronic diseases is 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity, aerobic activity is recommended each week, and muscle-strengthening activities (free weights or resistance bands) two or more days a week. It would be ideal for older adults to add balance training to the mix. If it’s challenging to find long periods of time to exercise, note that three 10-minute bouts or one 30-minute bout will deliver equal improvements in fitness.
Stretch before or after exercise?
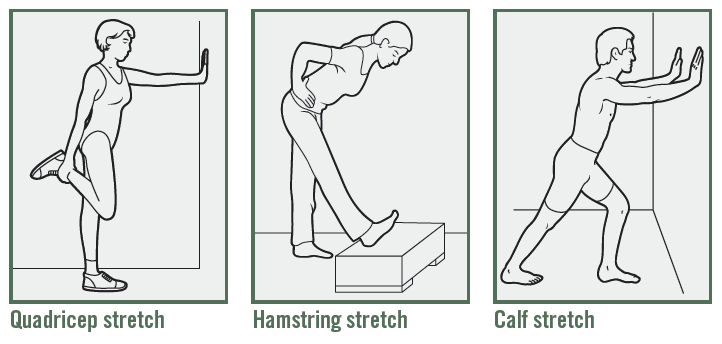
Before, after or both can all work well, if done properly. Do not attempt long stretches beforehand when your muscles are cold and you’re likely to pull a tendon, cautions Christine Butz, Doctor of Physical Therapy at Athletico. Instead, take 10 minutes to pedal on a stationary bike, march in place or walk around. Post exercise is the time for long, 30-second stretches that help you slowly increase muscle length (see below for examples). Most importantly, don’t push through pain, says Butz. “If you experience sharp, persistent pain, or have difficulty moving through a full range of motion, stop and see a physician to determine if it’s a strain, tear or fracture.”
Steady state or interval training?
Once the bastion of elite athletes, interval training can be used at any level, according to Mayo Clinic. Simply alternate short bursts (approximately 30 seconds) of intense activity with longer intervals (three to four minutes) of less intense activity. For instance, if your exercise is walking, try incorporating a brief surge of jogging into your regular walks or alternate leisurely strolling with periods of brisker walking. As your cardiovascular fitness improves, you’ll be able to exercise longer or with more intensity during your spring fitness routine.
What are the best activities to try?
Tap into one of these fitness trends to reinvigorate your workouts:
- Starting with Jazzercise in the 1980s, and rising again in the 2000s with Zumba, both of which remain popular, numerous dance-centric classes are offered at health clubs and park districts – Broadway show routines, tap dancing, belly dancing, Irish dancing, square dancing, line dancing and ballet-inspired barre workouts. Interesting note: a number of studies are in progress exploring the possible benefits of dance in enhancing cognitive function and reducing stress.
- Indoor cycling classes such as SoulCycle, Flywheel and CYC provide a fast-paced, high-energy environment. If you prefer to stay outdoors, but feel a bit unsteady on a 10-speed racer, check out the proliferation of classic cruiser bikes featuring wide, comfortable seats and upright handlebars.
- Yoga and Pilates. Both are low-impact workouts that focus on using bodyweight resistance. Yoga builds strength, balance (ideal for preventing falls) and harmony in mind and body, with breathing exercises, meditation and postures (asana or poses) that stretch and flex various muscle groups. Pilates is excellent for improving core strength and recovering after injury.
- Water classes are another low-impact option to build core muscles and help improve flexibility, stability and balance. Choices include traditional aqua aerobics as well as aqua ballet, aqua yoga and aqua tai chi.
- Functional Training classes are designed to improve balance, coordination, agility, speed and strength, such as BOSU (both sides utilized) ball workouts.
The post Spring Fitness appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.
by Ivan | Apr 2, 2019 | Medications, Patient News

Smoking Out the Myths: Medical Marijuana
Does medical marijuana offer a solution to treating epilepsy, chronic pain, anxiety and neurogenerative diseases? Or is it an untested, potentially unsafe treatment that will eventually turn out to be more of a pipe dream? As with so many of today’s biggest questions, the truth is somewhere in between. We bring you a down-to-earth view of this much-discussed and yet oft-misunderstood topic to separate the hype from the hope and dispel some Medical Marijuana Myths.
While the marijuana or hemp plant has been used for more than 3,000 years, research and treatment today is primarily focused on the extract known as CBD, a cannabinoid. Unlike one of the other chemicals in the plant, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol,) CBD has no psychogenic effects and does not produce the “high” commonly associated with marijuana. Hundreds of CBD-related tests are now in progress, and CBD products are available at dispensaries, online and are making their way into everything from coffee and yogurt to pet treats.
Last June, a major milestone was reached when the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the CBD drug Epidiolex for two rare, severe forms of treatment-resistant epilepsy. Epidiolex, along with dronabinol and nabilone (which are synthetic cannabinoids previously approved to treat nausea from chemotherapy that has not responded to standard therapy), are now the only FDA-approved cannabis-based drugs.
The FDA was careful to note about Epidiolex: “This approval serves as a reminder that advancing sound development programs that properly evaluate active ingredients contained in marijuana can lead to important medical therapies. Controlled clinical trials testing the safety and efficacy of a drug, along with careful review through the FDA’s drug approval process, is the most appropriate way to bring marijuana-derived treatments to patients. Because of the adequate and well-controlled clinical studies that supported this approval, prescribers can have confidence in the drug’s uniform strength and consistent delivery.”
High hopes
The FDA’s cautionary tone was necessary because of the many well-publicized clinical and preclinical trials underway to test marijuana and its extracts. Interest continues to grow, as evidenced by the numerous research projects in progress. The most prominent studies are focused on chronic pain, trying to evaluate whether marijuana is a safer and less addictive alternative to opioids.Other research is aimed at testing if cannabinoids improve the symptoms of multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, anxiety and insomnia, as well as its potential role in anti-inflammatoryand antiviral activity, blocking cell growth and preventing the growth of blood vessels that supply tumors.1
As promising as the research appears, it’s important to realize that at this time, not enough large, clinical trials have been conducted to show that the benefits of marijuana outweigh the potential risks. Research is still preliminary and much remains unknown about CBD and other cannabinoids’ optimal dosing range and the best route of administration (by mouth, inhaled, topically or sprayed under the tongue). Importantly, because they are not FDA-approved, the levels of THC or CBD can differ greatly from one dispensary to another or one batch to another.
Side effects are also hard to predict because potential impurities and variations in dosage are not addressed as they are in all FDA-regulated products. We are only starting to evaluate side effects which may range from minor dry mouth and dizziness, to death. It is also unclear if the products interact with other medications. An added concern is that older and sicker people may be more vulnerable to the drug’s side effects.
Our bottom line: although CBD is readily obtainable in most parts of the United States, and laws legalizing its use for medicinal purposes continue to pass, we need to take a step back and realize the process is far from complete. The fact is the scientific evidence does not yet support many of the claims to ease symptoms of certain diseases, improve quality of life and relieve pain, nor has it been approved for use as a cancer treatment. As Cleveland Clinic’s head of Employee Health Services recently pointed out, medical marijuana has not yet undergone extensive clinical trials, public hearings and approval by the FDA, or been thoroughly tested for safety and efficacy. His recommendation is one we can all support – focus on research that isolates specific compounds found in marijuana, produces a dose-specific medication, and submit it to testing and regulatory processes.
1 National Cancer Institute, 2019
Did You Know?
330
Number of cannabinoid research projects supported by the National Institutes of Health in 2017
34
Number of states (including the District of Columbia) that have approved the medical use of cannabis as of 2018
The post Medical Marijuana Myths appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.
by Ivan | Apr 2, 2019 | Medical Conditions, Patient News

Attention Please: ADD/ADHD is Not Just a Childhood Condition
In the 21stcentury, it’s standard procedure to test unfocused, impulsive and restless children who struggle to achieve in school for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and provide support and treatment well into adulthood. But for those who came of age prior to the 1970s, that diagnosis was rarely made, leading to a lifetime of challenges. Only now, as ADHD and ADD are recognized as conditions that often do not disappear with maturity, are some seniors finally finding the answer to problems that have haunted them for years in Adult ADD.
ADD is a condition of varying degrees, and in cases of milder severity, whether in the young or older patient, can be difficult to diagnose; especially in older adults, because the symptoms are different than in children. Hyperactivity is rarely the primary indicator, although remnants are felt such as restlessness and talking too much. Most frequently experienced by adults is a tendency to be easily distracted, a decline in working memory and a lack of focused attention. As we get older, the challenge may lie in distinguishing these issues from the normal aging process, mild cognitive impairment or early dementia. Forgetting names, misplacing things, or having problems with organization and planning can be hallmark traits of ADD or an aging brain. The key to identifying the difference is longevity of symptoms. ADD doesn’t suddenly appear full-blown in an adult, but leaves a years-long trail of distraction in its wake.
What are Symptoms of Adult ADD?
Experts advise that symptoms can shift with age, but these are found fairly consistently in older adults with ADD*:
- “Swiss cheese memory,” characterized by things that slip through the cracks
- Issues with working memory, such as being easily thrown off course mid-task
- Misplacing items
- Forgetting words or names, brain going ‘blank’ periodically
- Difficulty learning new things
- Talking excessively, often without realizing it
- Interrupting others
- Trouble following conversations
- Difficulty maintaining relationships and keeping in touch
According to the organization ADDitude, a leading source of information, support and advocacy for people living with ADHD, asking this simple question – “Would you have been talking about these symptoms 20 years ago?” – can be one of the most accurate of all indicators. Patients who answer in the affirmative, remembering constantly being chided for a messy room, branded as a daydreamer or underachiever, and finding it difficult to keep organized and on time at a first job, are more likely to have previously undiagnosed ADHD. In fact, the majority would say “I can’t remember a time that I wasn’t this way.”
Gratifyingly, adults who are diagnosed with ADHD or ADD in their older years find it can be revelatory to finally identify the cause of their ongoing challenges, and receive the support they need at a particularly vulnerable life stage. Coping with ADD as a senior actually parallels the issues faced by young people with ADHD when they leave home. The loss of structure for both groups can strain their ability to adequately care for themselves, and poor sleeping or eating habits can result, which exacerbate ADHD symptoms. However, treatment which may include appropriate doses of stimulant medication and cognitive behavioral therapy, has been shown to work as well for adults as children, and provide a newfound satisfaction with life.
As Dr. David W. Goodman, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and director of the Adult Attention Deficit Disorder Center of Maryland, explains: “People may ask, ‘if you’ve had this problem for so long, why bother treating it now?’ Imagine you believed yourself to be as others labeled you throughout your life – careless, irrational, a daydreamer, dumb or just plain odd. Then, you realize a treatable disorder caused these symptoms, and they aren’t a reflection of who you are. It’s liberating to understand the difference between what you have – a disorder – and who you are – a person.”
*Source: Kathleen Nadeau, Ph.D. presentation at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the American Professional Society of ADHD and Related Disorders
Did You Know?
Although ADHD and ADD is a commonly seen psychiatric condition in the US, second only to generalized depression, adults in their 50s, 60s and 70s often go undiagnosed and untreated.
Fewer than half of adults with ADHD ages 45+ have ever sought any kind of treatment and only 25% have tried medication.
Source: www.additudemag.com
The post Adult ADD appeared first on Specialdocs Consultants.









Recent Comments