
by lduque | Jan 11, 2022 | Medical Conditions, Patient News, Wellness
Coping With Sad This Winter
As we continue to weather the storm of COVID-19, seasonal affective disorder, or SAD, is once again on our radar. More subtle than an arctic blast, SAD is just as real, with just as much potential to have a chilling effect on our mood, productivity and wellness. Similar to last winter, the emotional stress and ongoing uncertainty that come with a global pandemic is unfortunately creating an ideal climate for SAD. Not surprisingly, mental health experts are expecting to diagnose and treat an increased number of people with SAD in 2022.
First discovered in the 1840s, SAD was not officially recognized as a disorder until the early 1980s, when Dr. Norman Rosenthal coined the term and categorized it as a form of clinical depression. We now know that SAD affects at least 5% of Americans; is more likely to affect women than men, those with other forms of depression or family members with the condition; and is far more common in northern regions, due to reduced natural sunlight. New research has advanced several theories as to why some people develop SAD, including: sluggish transmission of serotonin (which helps regulate mood and the body’s circadian rhythms; reduced sensitivity of the eyes to environmental light; a combination of these factors; or other reasons yet to be uncovered).
A deeper understanding of what triggers SAD and its impact on mental health has inspired a growing number of clinical treatments that can effectively neutralize its effects.
Chief among them:
Healing light.
Sitting in front of a bright light box for 30 to 45 minutes daily has been a treatment of choice for more than three decades, helping SAD patients with either 10,000 lux of white fluorescent or full spectrum light that shines 20 times brighter than ordinary indoor illumination. Dawn simulation, another form of light therapy, begins in early morning before patients awake by emitting a low level of light that gradually increases over 30 to 90 minutes to recommended room light level (approximately 250 lux). Enhancing indoor lighting with regular lamps and fixtures is also recommended).
Talk therapy.
Newer studies from the University of Vermont suggest that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), a psychological treatment aimed at providing patients with tools to change negative thoughts and behaviors, may be as effective as light therapy for treating SAD. According to the National Institute for Mental Health (NIMH), CBT adapted for SAD focuses on behavioral activation, helping SAD sufferers identify and engage in enjoyable seasonal activities to combat the ennui and fatigue they typically experience in winter.
Sleep hygiene.
Creating a consistent light-dark, sleep-wake cycle is important for SAD patients, who often experience hypersomnia (excessive daytime sleepiness) and insomnia (trouble falling or staying asleep).
Antidepressant medications. Because SAD is associated with disturbances in serotonin activity, antidepressant medications have been effectively used to treat symptoms.
Active days. Keep moving with daily walks outside, even on cloudy days, and aerobic exercise. Both can help alleviate symptoms of SAD.
Winterize your mental health
Be proactive in safeguarding your mental wellness over the coming months. Most importantly, know the symptoms of SAD and call our office for help if you’re experiencing:
- Diminished interest in things that were once enjoyable
- Low energy or overwhelming fatigue
- Difficulty with concentration or focus
- Worthless or helpless feeling
- Sleep issues: too much sleep, or not enough
- Changes in appetite or weight; increases in carbohydrate and sugar cravings
- Agitation
Experts advise those who’ve previously experienced episodes of seasonal depression to try to get in front of it this year. Call our office for guidance regarding medications or CBT sessions. For many, reprogramming their mindset can help restore proper circadian rhythms and eliminate the psychological dread of winter. Try enrolling in an online class, taking up a new hobby or creating a new routine to optimize daylight exposure. Or keep it even simpler. As Dr. Rosenthal told the New York Times, “A 20-minute early morning walk in the sun can be as good as commercial light therapy.”

by lduque | Dec 15, 2021 | Patient News, Staying Active, Wellness
How to Replace Bad Habits with Healthy, Sustainable Behaviors
For entrepreneur physician Kyra Bobinet, MD, the typical reasons behind a failed diet served as the impetus for developing a novel approach to behavior change.
“I was doing so well. I knew what to eat, when to eat, how to eat, and then I just stopped doing it…and I don’t know why.”
Her answer to a patient’s familiar lament above, called the Iterative MindsetTM, is now used by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to enhance its diabetes prevention program.
Drawing on her neuroscience and medical training at the UCSF School of Medicine and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Bobinet conducted years of field research aimed at eliminating the inevitable gap between intention and action. What she discovered was a way to change even the most intractable bad habits and permanently replace them with healthy, sustainable ones.
The Iterative Mindset, Bobinet asserts, is the key to people who succeed despite seemingly insurmountable odds. In her early work helping frontline Walmart employees manage conditions such as obesity, cardiac disease and diabetes, she observed that only a small percentage of people were able to achieve the necessary lifestyle changes. Notably, they faced every possible headwind of financial and social stress – single parenting, senior caregiving, food insecurity and lack of healthcare access.
“Nonetheless, they somehow were able to lose weight, get off their medications, and dramatically improve their health,” she recounts. “We looked and looked, but the only common link between them was the Iterative Mindset, a resilient way of approaching behavior change like an experiment – with curiosity, innovation and no failure or blame if it doesn’t work out as planned.”
It’s a stark contrast with the way most people view their failure to change longstanding habits. Bobinet describes why: “The habenula, a recently characterized area of the thalamus, has two functions – detecting failure and then, if you think you failed, suppressing your motivation to keep trying. By activating whenever you believe you’ve failed to reach a goal, the habenula places you in a state of learned helplessness, associated with higher depression and low self-efficacy. This is when most people give up and bad choices ensue.”
She posits that those who form new habits by continually trying again in different ways, or iterating, are able to bypass that switch in the brain. An iterative mindset can succeed where the performance mindset, used for SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-based) goals or tracking steps with wearable devices, sometimes cannot.
“Performance mindset works well to motivate for tasks that are short-lived, and for optimization, such as athletes who have already experienced a substantial success and want to strive for the next level,” says Bobinet. “However, it can be detrimental when used to modify behaviors in more vulnerable people, setting them up for an eventual win or lose situation that triggers feelings of failure and causes loss of motivation to keep trying.”
True change only happens when a new behavior turns into a habit, repeated so frequently it grows to be automatic, and by definition becomes part of your lifestyle, says Bobinet. The process can take up to two years, with multiple relapses an expected part of the process.
“It’s completely natural to relapse when you’re stressed or distracted; it’s how fast you get back in motion that counts. And you cannot fail as long as you iterate,” emphasizes Bobinet. “Don’t blame yourself, blame what you tried—it wasn’t the right thing right now. Think of it as an experiment that needs tweaking and continue to version until you find the right fit for you.”
If you’re interested in trying this mindset approach to behavior change, Dr. Bobinet offers a free basic Fresh Tri app through the Apple App Store and Google Play.

by Specialdocs Consultants | Dec 15, 2021 | Patient News, Wellness
In the spirit of starting 2022 with healthy intention, we’ve taken a page from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) latest recommendations, long considered the gold standard for clinical preventive services, and prepared the following proactive guide to staying well in the new year.
Back in 1903, Thomas Edison predicted where we were headed: “The doctor of the future will give no medicine but will instruct his patient in the care of the human frame, in diet, and the cause and prevention of disease.”
While we have yet to reach the future envisioned by Edison, preventive care, relegated to the back seat during the pandemic, is in full gear once again.
Since 1984, the USPSTF team of volunteer, independent experts in internal medicine, family medicine, pediatrics, behavioral health, obstetrics/gynecology and nursing has conducted rigorous assessments of the scientific evidence for the effectiveness of a broad range of preventive screening, counseling and medications. Their findings, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, laid the foundation for preventive medicine in primary care, from when to get your first colonoscopy to whether an aspirin a day is really the best way to keep a heart attack at bay.
A number of USPSTF recommendations have changed significantly over the years, guided by evolving science and clinical experience. In 2021, these changes included lowering the screening age for diabetes from age 40 to 35, lowering the age for colorectal cancer screening from age 50 to 45, and strongly discouraging people over 60 from taking a low-dose aspirin each day to prevent a first cardiovascular (CV) event. As recently noted by the advisory board, this doesn’t represent a flip-flop or misfire, but rather necessary updates based on new research. So, for example, when the latest evidence showed the increased risk of gastrointestinal or brain bleeds in certain populations from taking a daily aspirin to prevent CV disease, the panel reviewed, reconsidered and drafted a revision to its 2016 recommendation. Similarly, when data pointed to the incidence of diabetes increasing at age 35 and the benefits of lifestyle interventions for reducing progression from prediabetes to the more serious type 2, the USPSTF revised accordingly.
What’s on the radar for the USPSTF? Recommendations being studied now for potential updates include statin use for the prevention of CV disease; vitamin, mineral and multivitamin supplementation to prevent CV disease and cancer; behavioral counseling interventions for prevention of CV disease in low-risk adults; hormone therapy to prevent chronic conditions in postmenopausal women; effectiveness of screening for depression, eating disorders, obstructive sleep apnea, skin cancer, osteoporosis, glaucoma and atrial fibrillation; and a comparison of breast cancer screening methods. Stay tuned for new developments.
An Ounce of Prevention
Following are the latest USPSTF preventive medicine recommendations, intended for people without symptoms of the disease. As always, please consult with your healthcare provider for guidance based on your personal health situation.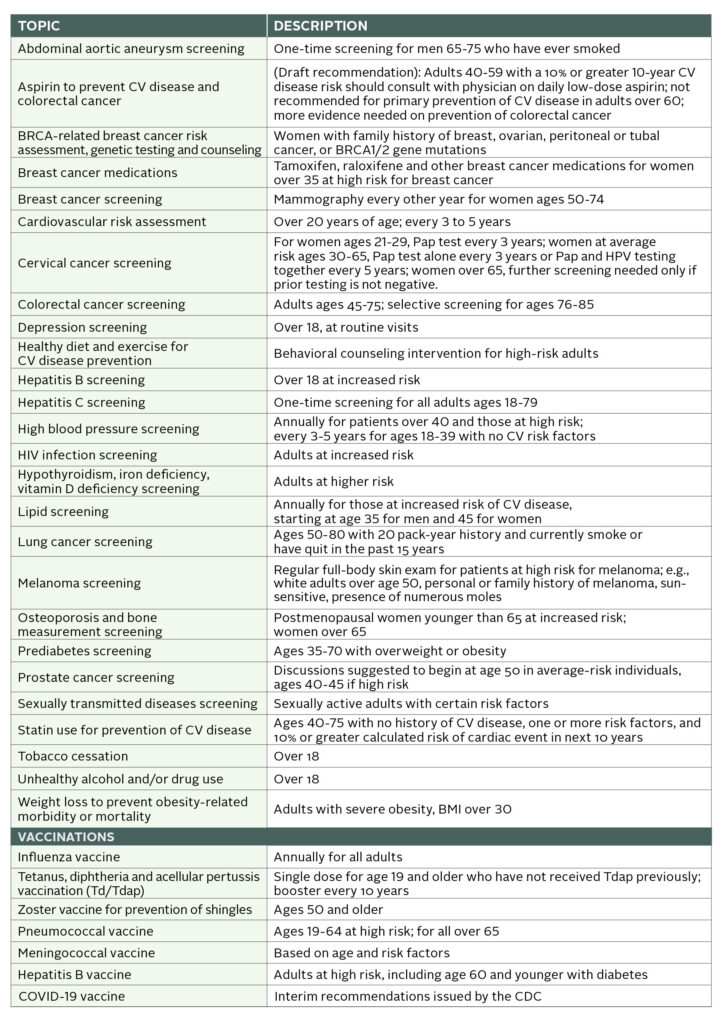

by Specialdocs Consultants | Dec 15, 2021 | Nutrition, Patient News, Wellness
Eating Your Fruits and Veggies May Help Reduce the Risk of Chronic Disease
Fill your plate with a vibrant, colorful array of fruits and vegetables for a naturally delicious way to meet your daily requirement of vitamins, minerals and nutrients. Plant foods contain thousands of natural compounds called phytonutrients, which may have anti-inflammatory benefits that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Every color has a contribution to make – aim for a few different ones each day, and enjoy the entire spectrum.
Red and pink:
These fruits and vegetables are an abundant source of the carotenoid lycopene, which may help balance free radical activity in the body, offering protection against prostate cancer and heart and lung disease. Additional picks: red onions, persimmons and raspberries.
- beets
- cherries
- cranberries
- pink grapefruit
- pomegranates
- radicchio
- red radishes
- red apples
- red grapes
- red peppers
- red potatoes
- rhubarbs
- strawberries
- tomatoes
- watermelons
Orange and yellow:
Enjoy an extra boost of beta cryptoxanthin, which supports intracellular communication and may help prevent heart disease. Orange and yellow fruits and vegetables also contain vitamin C and carotenoids, including beta-carotene, which is associated with promoting healthy vision and cell growth. Additional picks: pomelos, turmeric root and star fruit.
- acorn squash
- butternut squash
- apricots
- cantaloupes
- carrots
- corn
- grapefruit
- lemons
- mangoes
- nectarines
- oranges
- orange peppers
- papayas
- peaches
- pineapples
- pumpkins
- summer squash
- sweet potatoes
- tangerines
- yams
- yellow apples
- yellow peppers
- yellow squash
Green:
These are some of the healthiest fruits and vegetables, rich in chemicals like sulforaphane, isothiocyanates and indoles, which may inhibit the action of carcinogens. Dark green and leafy vegetables have the highest concentration of both antioxidants and fiber. They’re also packed with potassium, lutein, isothiocyanates, isoflavones and vitamin K, which can be important for vision, bone and blood health. Greens like kale have as much calcium as milk. Additional picks: Swiss chard, arugula, zucchini, edamame, alfalfa sprouts and green herbs (mint, rosemary, sage, thyme and basil).
- artichokes
- asparagus
- avocados
- bok choy
- broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- celery
- collard greens
- cucumbers
- green beans
- green cabbage
- green grapes
- green onions
- green peppers
- kale
- kiwis
- leeks
- limes
- mustard greens
- okra
- pears
- peas
- romaine lettuce
- snow peas
- spinach
- sugar snap peas
- watercress
- zucchini
Blue and purple:
Anthocyanins – powerful antioxidants that may help delay cellular aging, block the formation of blood clots and boost urinary tract health – abound in these fruits and veggies. Additional picks: beetroot, radishes and purple cabbage.
- blackberries
- blueberries
- black currants
- dates
- eggplants
- grapes
- plums
- prunes
- purple figs
- raisins
White:
These foods may not be as brightly hued as the others, but they shine with valuable phytonutrients. These include the potentially anti-tumor properties of allicin and quercetin, found in garlic and onions; the healthy compound sulforaphane in the cruciferous cauliflower; and immune-supporting selenium in mushrooms. Additional picks: leeks, white beans (cannellini, navy beans, lima beans, soybeans), lychees, white peaches and daikon radish.
- bananas
- cauliflower
- garlic
- Jerusalem artichokes
- mushrooms
- onions
- potatoes
- parsnips
- shallots
Sources: American Heart Association, Rush.edu, Harvard Health
ul.multi-col {column-count: auto;column-gap: 2em;column-width: 18ch;}

by | Sep 11, 2021 | Nutrition, Patient News, Wellness
How to Pare Down Protein & Cut Back Carbs
Inspired by a belief that our diets can be redefined to integrate both healthier eating and environmental responsibility, Menus of Change encourages a meaningful “flip” in the emphasis on animal proteins and highly processed carbohydrates to an emphasis on highly appealing alternatives.
Menus of Change, a collaboration of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Culinary Institute of America (CIA), authors a creative approach to enjoying delicious, nutritional and sustainable foods: “The Protein Flip” and its companion, the
“Carbohydrate Flip.”
The Protein Flip, introduced in 2016, laid the groundwork for the Menus of Change health- oriented methodology, stating, “Higher intake of red meat, irrespective of its total fat content, increases risk of heart disease, stroke and diabetes when compared to poultry, fish, eggs, nuts, or legumes.”
The Menus of Change solution was to challenge chefs in every setting to place meat, poultry and seafood in a supporting role or as a side and make vegetables and plant proteins the stars – for example, burger blends composed of primarily mushrooms, other vegetables, grains or legumes; surf and turf reimagined as seafood with bountiful vegetables and only a bite or two of meat; use of tapas, mezze and other plant-forward small plate replacements for entrees. The public response was immensely gratifying, spurring further innovation and the mainstreaming of vegan options, such as lentil, barley and black bean burgers or wild rice polenta burgers made with mushrooms, carrots and leeks.
Building on their successful work with proteins, the collaborative is now developing a complementary program centered on advancing carbohydrate quality on the American plate. “From fluffy pancakes to soft hamburger buns, refined, fast-metabolizing carbohydrates are still found in many a diet and are contributing to the rise in diet-linked chronic conditions such as
diabetes and heart disease,” according to a recent Menus of Change summit panel discussion headed by Sarah Schutzberger, RD, CSO (certified in oncology nutrition). “In large part because of our food choices, scientists project that 75 percent of chronic diseases are attributable to diet and lifestyle.”
A substantial emphasis on whole, minimally processed carbohydrates can help change the trajectory, beginning with these flips described by the panel:
- Take on the Three Pleasures challenge: Create a delicious dessert using dark chocolate, nuts, and fresh-cut or dried fruit. “Instead of forcing a choice between a whole slice of cheesecake with a single strawberry as garnish or a plain bowl of berries, enjoy a dessert made from a healthy market basket that includes dark chocolate, fruit, whole grains, nuts and yogurt,” advised Greg Drescher, Culinary Institute of America.
- Look to world food cultures for inspiration:
- Mediterranean region: “This type of cooking features a healthy fat versus a low fat approach to diet, with olive oil as the foundation of flavor,” said Drescher. Try tabouli, made of cracked bulgur wheat, chopped parsley and olive oil, or a salad made with hydrated, whole-grain barley rusks, topped with chopped tomatoes and fresh feta cheese and tossed with olive oil. Also important: improve the health profile of pasta by using a whole-grain type and cooking al dente to make it a source of slower-releasing carbohydrates.
- France: The niçoise salad suggests ways to include potatoes in limited amounts by pairing with green beans and other vegetables, hard-boiled egg, and a light vinaigrette for a slow-metabolizing lunch.
- Asia and India: Try a salad featuring soba noodles made from buckwheat flour; a Buddha bowl with foundational ingredients that include legumes, fresh vegetables and plant proteins, paired with small amounts of salmon or roasted tofu; and whole-grain flatbreads.

by | Sep 11, 2021 | Medical Conditions, Patient News, Wellness
From Boosters & Breakthroughs to Vaccines & Variants: Where Do We Go From Here?
The following reflects an 8/24/2021 discussion; please check the CDC website for real-time updates as the situation continues to evolve.
Their answers may not land lightly, but epidemiologist Jodie Guest, PhD, and drug development expert Michael Kinch, PhD, have been immersed in examining COVID-19 since its first stirrings in early 2020. They share an informed look at the road ahead for us all.
State of Concern
Noting more than 39 million COVID-19 cases nationwide, (as of 9/2/21) Guest projects this will continue to rise rapidly and eclipse one million a week. While “hot spots” for outbreaks clearly correspond to the country’s most lightly vaccinated locales, the impact of the delta variant is being felt in virtually every state. “There’s almost nowhere you can go in the U.S. that you don’t need to be masked indoors, even if vaccinated,” she says. The progressive increase in vaccinated patients with COVID-19 in European hospitals is also troubling, says Kinch, a potential harbinger of what is to come for the U.S.
However, what’s driving the surge is not cases among the vaccinated, known as “breakthroughs.” It’s a term Guest would like to eliminate permanently, given its negative connotation regarding vaccine efficacy. “These type of infections are still rare. More than 90% of those hospitalized with COVID-19 are unvaccinated.” She points out that while viral loads in patients with COVID-19 are the same for vaccinated and unvaccinated patients in the first few days of illness, they drop much faster and further in the vaccinated.
The vaccine, contends Kinch, was never intended to eliminate all possibility of getting COVID-19. “It’s not a suit of armor,” he says, “because no vaccine ever provides 100% protection. But we know they work incredibly well to prevent you from getting very sick or dying.”
The FDA’s recent approval of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine, with Moderna approval expected to follow soon, is pivotal, says Guest, in helping launch vaccination requirements at businesses, schools and other locations. “Don’t underestimate the importance of this approval in providing support for mandates that will protect all of us,” she says. “Recognize that in the entire history of vaccines, there has never been a set more studied than the ones we have now.”
Adds Kinch, “With the enormous amount of data gathered on the vaccines’ efficacy and safety, those who think of themselves as vaccine hesitant may more accurately be described as vaccine resistant.”
Third Doses and Boosters
The recent approval of a third dose of Pfizer or Moderna for immunosuppressed patients who didn’t build sufficient immunity from the first two doses applies to just 3% of the adult population. For everyone else (with the exception of pregnant women), a booster shot six to eight months after the initial series is being considered for approval.
“Right now, that’s how long we believe we can go without significantly diminished immunity,” says Guest. Antibody tests are not proven to be an accurate measure of protection from COVID-19, says Kinch, because the antibody levels vary by individual.
If you received Pfizer or Moderna initially, choose the same for a booster. Notes Kinch: “There’s no difference between these two vaccines—one is not better than the other.” In fact, some studies show no impact on efficacy from switching brands, he says; Johnson & Johnson data is yet to come.
And where does the flu shot fit in this fall? Absolutely essential, both agree, with the only caution that a two-week separation between the two vaccines may be recommended by some healthcare providers to avoid triggering a hyperactive immune response.
Protecting our Children
The best way to keep youngsters under 12 safe is ensuring that everyone around them is vaccinated, says Guest.
“Teachers, caregivers, babysitters and others should be vaccinated, or fully masked whenever they’re with children,” she advises. A different dose is being tested for 5- to 12-year-olds, with approval possible later this year.
The Next Wave of Variants?
While not identified by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) as a “high concern,” Kinch admits that the lambda variant worries him primarily because not enough is known about its ability to resist vaccines. “One view is that the COVID-19 spike protein can only mutate to a certain point, and if that’s true, lambda could be the end of the virus. The other view is that we don’t know if it stopped mutating,” he says.
“We’re not defenseless, though,” counters Guest, “because we can keep it from getting here by having COVID-19 not circulating in communities. Greater numbers of vaccinated people will prevent us from getting whatever variant might follow delta.”
Stay Safe and Well
One of last year’s most popular signoff lines takes on new resonance as our experts advise on what that now means for the vaccinated in fall 2021.
Mask Up, Indoors and Out.
Masks are increasingly needed outside in crowded areas. Indoors, remember that while a soft, comfortable cloth mask protects others from you, if you need extra protection in certain settings, use a KN95 or N95 mask.
Pass on Indoor Dining, Movies, Concerts and Sporting Events.
Also reconsider full-capacity outdoor events with no masking/distancing/vaccine requirements. (As an alternative, order take-out and support virtual events offered by local venues). And avoid getting together in person with those who are not vaccinated.
Reach out to Every Unvaccinated Person you Know.
“The best action we can take is to keep encouraging every unvaccinated person we know to get the shot, now,” advises Guest. “We’re all in the race against variants and need to work together to defeat them as quickly as possible.” Adds Kinch, “It’s unfortunate that the motivations behind much of the messaging has messed up the message itself. Be completely honest about what is known and not known about the vaccine.”
The Swiss Cheese Respiratory Pandemic Defense.
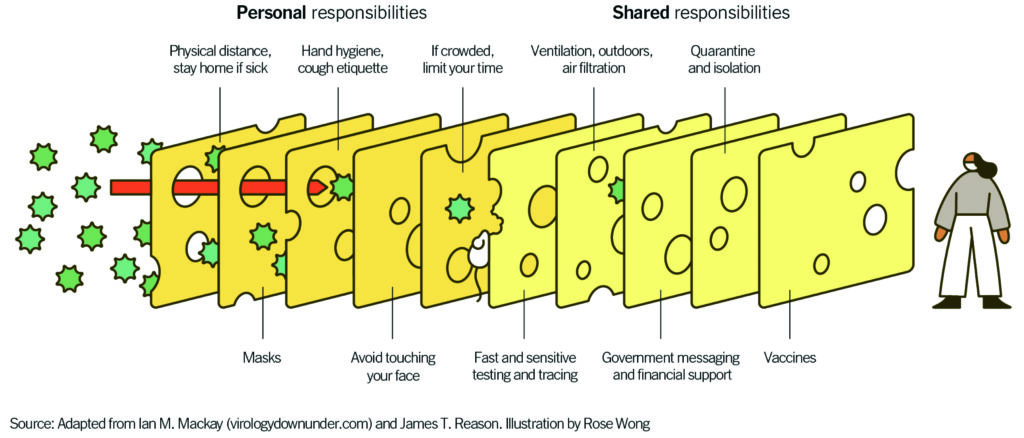 “Layering prevention messages is crucial because the delta variant has made the holes in the Swiss cheese slice of the vaccine just a bit bigger,” says Guest. “Now masks are more crucial than ever before.”
“Layering prevention messages is crucial because the delta variant has made the holes in the Swiss cheese slice of the vaccine just a bit bigger,” says Guest. “Now masks are more crucial than ever before.”
Dr. Jodie Guest is professor and vice chair of the Department of Epidemiology, Emory University, Atlanta, and award-winning leader of Emory’s Outbreak Response Team for COVID-19.
Dr. Michael Kinch is associate vice chancellor and founder/director of the Center for Research Innovation in Biotechnology and the Center for Drug Discovery at Washington University, St. Louis.








 “Layering prevention messages is crucial because the delta variant has made the holes in the Swiss cheese slice of the vaccine just a bit bigger,” says Guest. “Now masks are more crucial than ever before.”
“Layering prevention messages is crucial because the delta variant has made the holes in the Swiss cheese slice of the vaccine just a bit bigger,” says Guest. “Now masks are more crucial than ever before.”
Recent Comments